Medical condition
Melasma

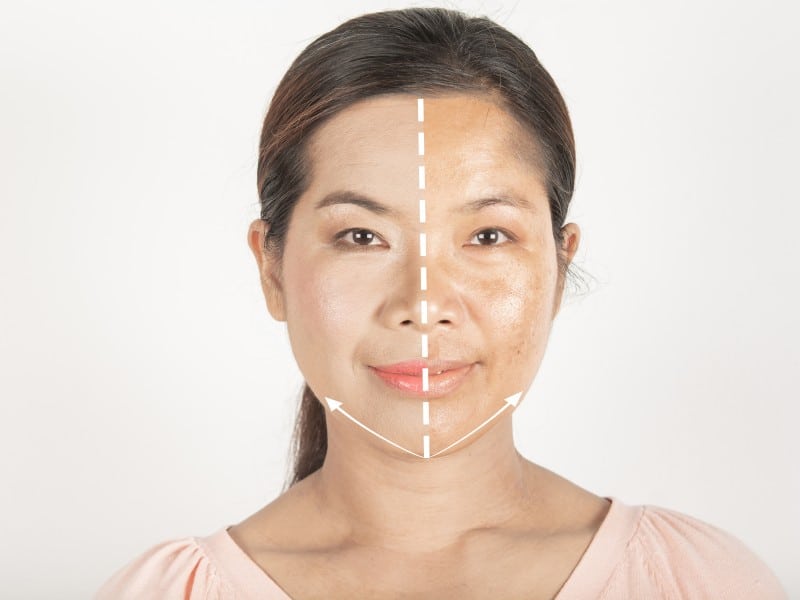
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition where dark patches or spots appear on the face. It happens more often in women and is linked to factors like genetics, hormones, and sun exposure. The patches are usually brown or greyish-brown and have a clear border. While it doesn’t cause physical harm, it can affect self-confidence.
Key Information
While it may not be possible to completely prevent melasma, there are measures that can help reduce the risk and minimize its occurrence or severity. Here are some preventive strategies
- Protect your skin from the sun by wearing a hat, seeking shade, and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.
- Try to avoid excessive sun exposure, especially during the peak hours of 10 am to 4 pm.
- Discuss the potential risks of hormonal treatments with Dr Tina if you're prone to melasma.
- Be cautious with cosmetics and scented products that may trigger melasma.
- Properly manage underlying conditions like thyroid disorders if you have them.
A combination of approaches is typically needed to manage Melasma effectively.
General measures:
- Protecting the skin from the sun all year round using a broad-brimmed hat and a high SPF sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection.
- Consider discontinuing hormonal contraception if possible.
Topical therapy:
- A successful treatment combination includes hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a moderate-potency topical steroid (skin lightening cream), which has shown improvement in 60-80% of cases.
- Other topical agents like azelaic acid, kojic acid, cysteamine cream, ascorbic acid, methimazole, tranexamic acid, glutathione, and soybean extract can be used alone or in combination.
Oral treatment:
- Tranexamic acid is an oral medication that can help inhibit factors involved in melasma by blocking certain processes.
Procedural techniques:
- Chemical peels and lasers can be used with caution, but there is a risk of worsening melasma or causing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Pretreatment with a tyrosinase-inhibitor like hydroquinone is recommended.
- Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHA) like glycolic acid or beta-hydroxy acids (BHA) like salicylic acid can help remove superficial pigment through chemical exfoliation.
- Microneedling, intense pulsed light (IPL), and various lasers (such as Q-switched Nd:YAG, ablative/non-ablative fractionated, and picosecond lasers) carry a high risk of relapse and increased resistance to treatment, so they should be performed by experts.
The exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of factors. It may be related to genetic predisposition and exposure to sunlight. Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or while using certain birth control methods, can also contribute.
Medications and scented products may trigger melasma in some cases. Researchers are studying various factors, including stem cells, nerves, blood vessels, and local hormones, to better understand how they contribute to the activation of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin.
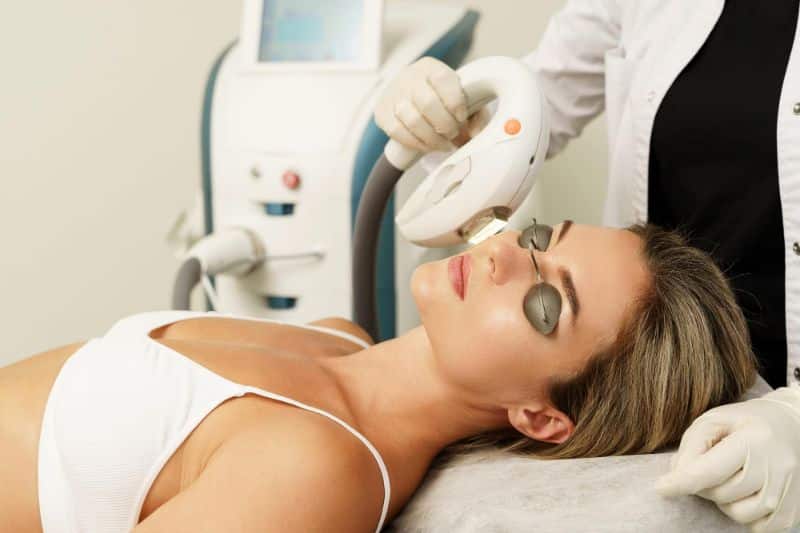
WHICH TREATMENTS ARE AVAILABLE?
Book in for a skin consultation with Dr Tina for an individualised treatment plan. Your best treatment will often depend on your age, gender, triggers and causes of your condition.
Dr Tina can advise on a combination including:
- Skin care advice
- Topical therapy
- Oral treatment
- Chemical peels and lasers
- Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHA) like glycolic acid or beta-hydroxy acids (BHA)
- RF Microneedling, IPL, and various lasers (such as Q-switched Nd:YAG).
Aftercare Instructions for Melasma
Lorem ipsum dolor
RESTORE YOUTHFULNESS
Schedule a Consultation
Call us on 07 3852 4878 or simply book an appointment

